Hepatitis is a serious and life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The Liver is a vital organ of our body, which is responsible for filtering toxins, aiding digestion, and storing energy. This condition causes inflammation in the liver. Hepatitis can occur due to viruses, alcohol, drugs, or immune system disorders. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approx 354 million people live with chronic Hepatitis B and C on a global level, and many are unaware of their infection.
This “silent disease” usually shows no symptoms until liver damage is advanced. Globally, this disease is responsible for more deaths each year than HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, or malaria. It is widespread, particularly in Asia and Africa, where the approach to screening and treatment is limited. Early detection, vaccination, and lifestyle changes are crucial in managing the disease. Hepatitis can be controlled with regular medical care, and serious complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer can be prevented.
Let's discuss below about hepatitis types, prevention, treatment, etc, in detail.
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a serious health condition that causes inflammation in the liver. The liver is the most important organ in the human body that is responsible for processing nutrients, breaking down toxins, and producing bile for digestion. In this disease, when the liver is inflamed, it cannot function properly, which leads to various health issues.
Hepatitis is classified into two classes: viral hepatitis and non-viral hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is caused by different strains of hepatitis viruses, including A, B, C, D, and E. Each virus spreads differently and affects people differently. On the other hand, Non-viral hepatitis is caused by alcohol abuse, drugs, toxins, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic conditions.
Hepatitis infection can be acute or chronic. Acute infection resolves on its own with proper care and treatment. Chronic infection can last for years and can cause liver damage, cirrhosis, or cancer. Symptoms that are commonly seen include fatigue, nausea, yellowing of the skin (jaundice), and abdominal pain, and in most cases, symptoms don't appear until severe liver damage occurs.
Types of Hepatitis
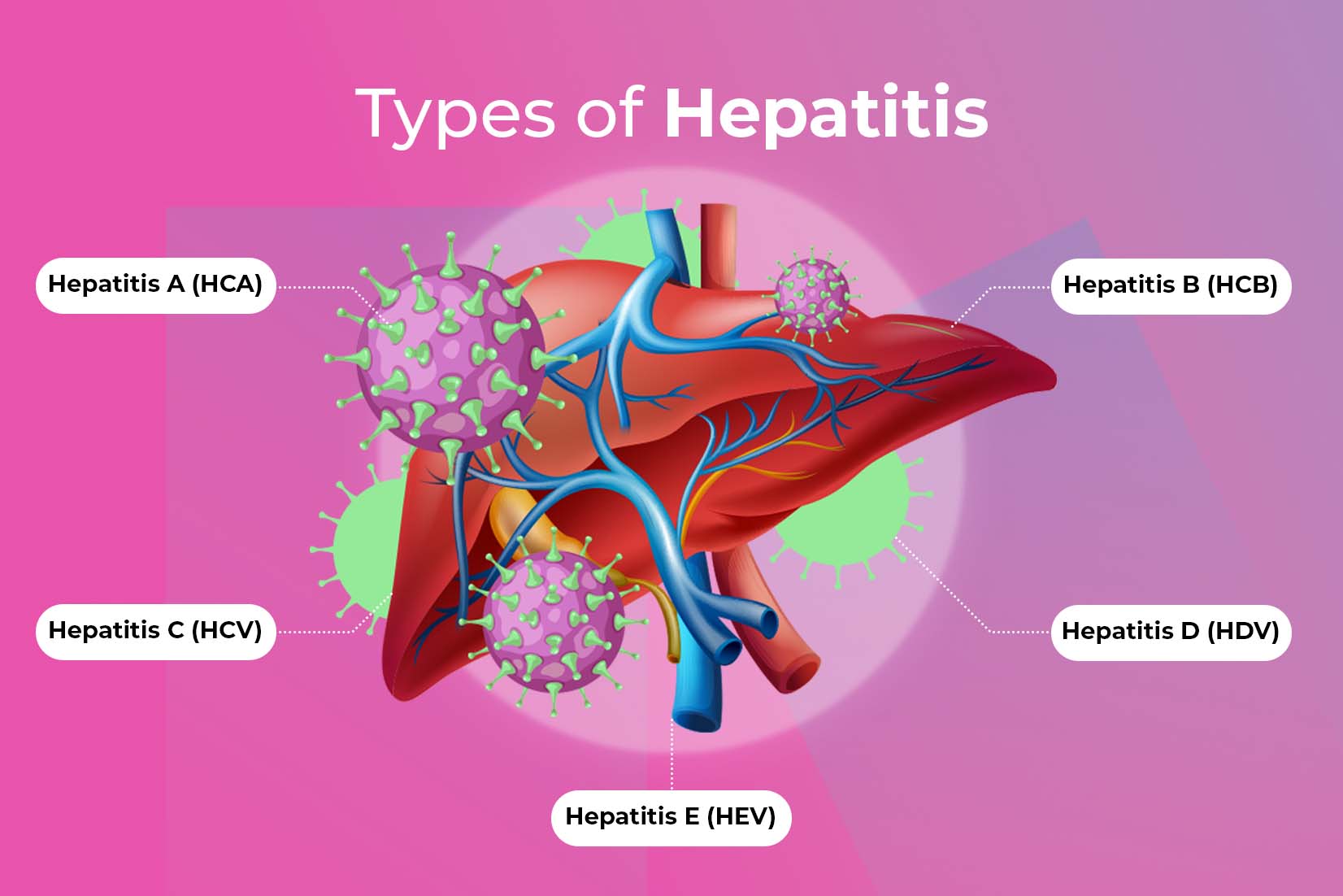
Types of hepatitis classified according to viral and non-viral hepatitis.
Viral Hepatitis
● Hepatitis A (HCA)
It can spread through contaminated food and water. This infection is usually short-term and does not cause chronic liver disease and It is preventable with good hygiene and vaccination.
● Hepatitis B (HCB)
It can be transmitted through blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Chronic HBV may lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. A safe and effective vaccine is available for this condition.
● Hepatitis C (HCV)
It mainly spread through contact with infected blood, such as unsafe injections, transfusions, or drug use and usually becomes chronic that lead to serious liver disease. There is no vaccine is available for it, but antiviral treatments can cure most cases.
● Hepatitis D (HDV)
It only occurs in people already infected with hepatitis B and it is more severe than HBV alone. It can be prevented by HBV vaccination.
● Hepatitis E (HEV)
Spread through contaminated water. It is common in developing countries. Usually self-limiting, but it can be dangerous for pregnant women.
Non-Viral Hepatitis
● Autoimmune Hepatitis: When immune system attacks the liver by mistake.
● Ischemic Hepatitis: Can be caused by lack of blood supply to the liver.
● Metabolic Hepatitis: Linked to fatty liver disease and metabolic disorders.
● Drug-Induced Hepatitis: Can triggered by certain medicines or toxins.
● Alcoholic Hepatitis: It caused by long-term heavy drinking.
Each type of hepatitis has different prevention and treatment strategies. Understanding the differences is essential for proper care and reducing the global disease burden.
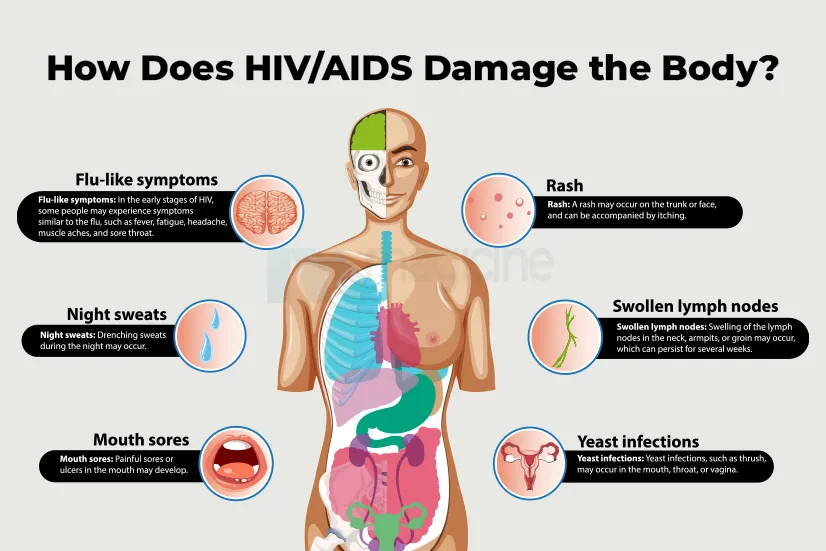
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis
Hepatitis symptoms depend on the type and severity of the disease. Some people notice while some don't notice any sign in the early stages. However, common symptoms include:
● Fatigue: A constant feeling of tired or weak always even after taking rest.
● Nausea and vomiting: feeling of sickness and loss of appetite
● Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to excess bilirubin in the blood.
● Stomach pain: Pain or discomfort, usually in the upper right side of the abdomen.
● Dark urine and pale stools: Signs of poor liver function.
● Fever and joint pain: Sometimes seen in viral hepatitis.
As these symptoms can overlap with other illnesses so hepatitis goes undetected until advanced stages. Therefore regular health checkups and diagnosis are necessary.
Complications of Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a life threatening condition and it can cause serious health complications if left untreated. There are the following conditions which can occur due to this disease:
1. Cirrhosis: It is the last stage of chronic liver disease. In this condition, long term inflammation damages healthy liver tissues by replacing them with scar tissue, blocking normal blood flow and affecting function. It can be caused due to hepatitis, alcohol consumption, and fatty liver disease. For prevention, early management, a healthy lifestyle and timely treatment is crucial.
2. Liver cancer: It is a serious disease and life threatening disease. Liver cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the liver start growing uncontrollably. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of this cancer. It is usually linked with chronic hepatitis B & C, cirrhosis, and fatty liver. Early detection and a healthy lifestyle can increase survival chances and increase prevention.
3. Chronic liver disease: It is a long term condition in which the liver becomes progressively damaged and reducing it's ability to work. There are various chronic liver diseases such as fatty liver, hepatitis, etc. and causes including alcohol abuse & autoimmune disorders. Continuous damage can lead to permanent loss of liver function and require lifelong treatment or liver transplantation.
How is Hepatitis Diagnosed?
Doctors use various methods to detect and confirm the disease:
1. Blood Tests: Blood tests like liver function tests (LFT) measure enzymes & proteins that can shows inflammation or damage. Viral serology tests detect the presence of hepatitis viruses and antibodies and PCR tests identify viral genetic material to measure viral load in the blood.
2. Imaging Tests: Imaging testing such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI can provide a detailed image of the liver. These tests can help to identify many liver diseases such as cirrhosis, tumors, or fatty liver changes.
3. Liver Biopsy: It is the method of detection in which small sample of liver tissue is removed to diagnose the disease. It helps doctors to determine the accurate liver damage and guide treatment plans.
Early diagnosis can save lives by allowing doctors to start treatment before severe complications arise. Regular check-ups are important for people who are at high risk such as healthcare workers, people with multiple blood transfusions, or those with a history of alcohol abuse.
Hepatitis Vaccination
Vaccination plays an important role in the prevention of hepatitis.
Hepatitis A Vaccine: This vaccine given in two doses and it is mainly for children & travelers of high-risk areas. It is a very effective vaccine and provides long term protection.
Hepatitis B Vaccine: This vaccine is given in three doses and it protects against both hepatitis B and D because HDV requires HBV to spread. This vaccine is included in routine childhood immunization programs.
Currently, there are no vaccines available for hepatitis C, D, or E, although research is ongoing. Vaccination remains one of the most effective public health strategies for reducing the issue of hepatitis worldwide.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis

The treatment for hepatitis changes based on type & severity:
1. Antiviral Medications:
Doctors give special antiviral medicinesfor the treatment of hepatitis B and C that help to get rid of the virus or keep it under control. New medicines called DAAs (Direct-acting antivirals) can cure more than 95 out of 100 people who have hepatitis C. People with long-term hepatitis B might need to take medicine for their whole life.
2. Lifestyle Modifications:
Don't drink alcohol or take harmful drugs because they affect liver functioning. Eat healthy food, do exercise, and keep a good weight and make sure your family gets vaccinated so they don't catch the virus.
3. Immunosuppressant:
Used in autoimmune hepatitis when your own body immune system starts attacking your liver by mistake.
4. Supportive Care:
For hepatitis A and E, you usually just need to rest, drink lots of water, and eat well.
5. Liver Transplant:
In the case of severe liver damage, transplant is the only option.
With modern treatments, many people with hepatitis can live long and healthy lives. Early treatment prevents complications and improves quality of life.
Latest Advances in Hepatitis Research
Research in hepatitis is getting advance rapidly. Scientists are working too on the vaccine for hepatitis C and E which can save millions of lives. New antiviral drugs are being developed to shorten treatment duration and reduce side effects. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR can target hepatitis B virus at DNA level and offer potential cure. Researchers are also studying immune-based therapies to enhance the body’s immune system to defense against the virus. Artificial intelligence and advanced imaging are helping doctors to detect liver damage earlier and personalize treatment plans. Global health programs are focusing on “hepatitis elimination” by 2030, aiming to expand testing, vaccination, and affordable treatment worldwide.
Conclusion
In today's time hepatitis is becoming a major global health challenge but it is preventable and treatable if diagnosed early with the right awareness. Understanding its causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward protecting your liver health. Vaccination, healthy lifestyle choices, and early diagnosis are essential in reducing the chances of this disease. With new medical innovation strategies, the future for people living with hepatitis is improving every year. By spreading awareness and supporting prevention programs, we can move closer to a world free from hepatitis.
There are many medicines available on the market to cure hepatitis but they are not cost effective. Magicine Pharma provide wide range of best quality antiviral medicines to treat Hepatitis B and C like Eltoplate 50mg Tablet, Revolade 25mg Tablet, Eltropag 25mg Tablet, Durataf 25mg Tablet, Elpag 50mg Tablet and many more at affordable price. You can visit their site to place your order and get your medicine at high discount price on fast home delivery.
FAQ
Q1: Can we cure hepatitis completely?
Some types of hepatitis, like hepatitis C, can be cured with antiviral medicines, while hepatitis B can be controlled but not fully cured.
Q2: Can hepatitis spread?
Yes, viral hepatitis can spread through blood, body fluids, contaminated food, or water.
Q3: Who should get vaccinated for hepatitis?
All children, healthcare workers, and people at high risk should receive hepatitis A and B vaccines.
Q4: Can hepatitis come back after treatment?
Hepatitis C does not return after successful treatment, but hepatitis B may comeback if not managed properly.
References
1. WHO – Hepatitis
2. CDC – Viral Hepatitis
3. Mayo Clinic – Hepatitis Overview
4. Liver Foundation – Types of Hepatitis