Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is one of the most studied diseases in the world. It has a major impact on human health. Across worldwide, millions of people are still living with HIV after significant advances in medicine. People usually think of HIV as a single viral type when they hear the term. However, HIV-1 & HIV-2 are two different forms of the virus.
Both types weaken the body's defenses mechanism against diseases and infections by affecting the immune system, especially the CD4 (T-helper) cells. HIV has the potential to turn into AIDS if left untreated.
Proper diagnosis, right treatment planning, and increasing global awareness are all needed along with knowing the difference between HIV-1 and HIV-2. Let's take a more detailed look at these two forms of HIV.
What Are the Types of HIV?
HIV is a retrovirus that belongs to the Lentivirus genus. It leads to a chronic infection that slowly weakens immunity. There are two forms of HIV strain known as HIV-1 and HIV 2. HIV-1 is the most common type worldwide. HIV 1 is more easily transmissible and responsible for the majority of infections. On the other hand, HIV-2 is less common and primarily found in West Africa. HIV-2 is less infectious and progresses more slowly than HIV-1.
Both spread similarly via unsafe sexual activity, sharing of needles, transmission from mother to child, and transfusions of blood. Their genetic composition, rate of transmission, worldwide incidence, and progression of the disease, however, differ.
HIV-1: The Most Common Strain
HIV-1 is the most common and dangerous form of the virus.Almost 90 percent of all HIV infections worldwide are caused by it.
- Origin: It is believed that it originated from chimpanzees in Central Africa and transmitted to humans in the early 20th century.
- Transmission: HIV-1 is highly infectious and spreads. It can easily through sexual contact, contaminated blood, and from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding.
- Progression: HIV has the potential to turn into AIDS if left untreated within 8–10 years after infection.
- Sub-types: HIV-1 has various subtypes like A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J, and K. Among these, Subtype C is common in India and Africa, while Subtype B is dominant in North America and Europe.
HIV-1 Characteristics:
- high rate of replication
- Sudden decline in the CD4 count
- Increase viral load
- rapid along with more severe disease progression
HIV-2: The Less Common Variant
HIV-2 is less common & usually less severe as compared to HIV-1. It was first identified in West Africa and is still primarily found there. While few cases have been reported across India, Europe, and the United States.
- Origin: HIV-2 most likely originated from sooty mangabey monkeys in West Africa.
- Transmission: Its mode of transmission is the same as HIV-1, but the transmission rate is much lower.
- Progression: People infected with HIV-2 usually seem to have lower viral loads. This type may take longer to progress into AIDS, sometimes over 15 years.
- Subtypes: Only A and B are epidemic out of eight known groups (A–H).
HIV-2 Characteristics:
- Slower disease progression
- Lower viral load
- Reduced efficiency of sexual transmission
- Fewer cases globally
Key Differences Between HIV-1 and HIV-2

Feature | HIV-1 | HIV-2 |
Worldwide Prevalence | About 95% of HIV cases worldwide with this strain. | It is primarily found in West Africa. |
Virulence | It is highly virulent and more aggressive. | This type is less virulent and has slower progression. |
Transmission Rate | High rate of transmission | Low rate of transmission |
Progression to AIDS | It takes about 8–10 years to develop from HIV to AIDS. | It may take 15 to 20 years or longer to develop from HIV to AIDS. |
Viral Load | High viral load found in patients infected with HIV-1. | Low viral load found in patients infected with HIV-2. |
Drug Resistance | This strain responds well to most ART drugs. | This strain is naturally resistant to some drugs (NNRTIs) |
Sub-types | It has nine sub types like A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J, and K. | It has eight known sub types(A–H). |
Mortality Rate | It is easier to detect. | Sometimes this strain is missed by standard HIV-1 tests. |
Because of such variations, accurately identifying the form of HIV is essential to providing proper treatment and care.
Symptoms of HIV-1 vs HIV-2
As HIV-1 and HIV-2 both affect the immune system's functioning. Both cause similar symptoms. However, there may be variations in the severity and duration of symptoms.
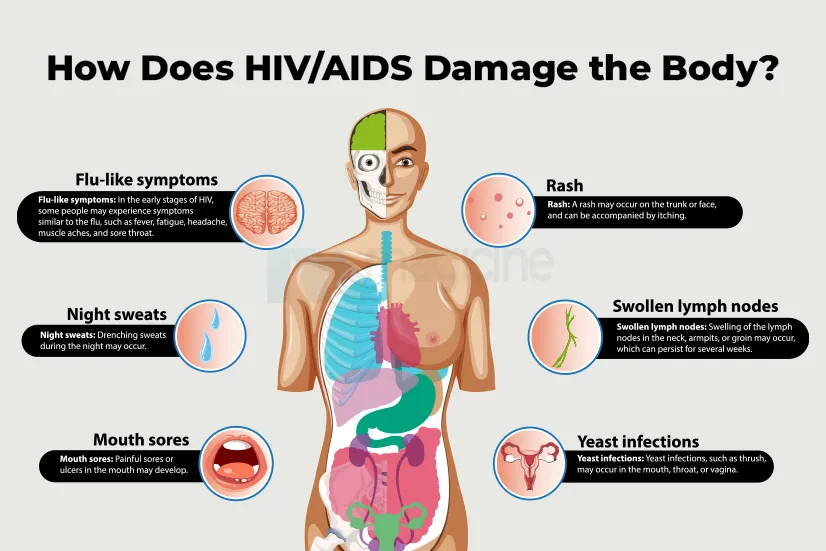
Acute HIV infection (early stage)
During the initial 2 to 4 weeks, a person with either HIV-1 or HIV-2 may experience a flu-like illness. Symptoms can vary in severity, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Common symptoms for both HIV-1 and HIV-2 in this stage include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Tiredness
- Muscle aches
- Rash
- Swollen lymph nodes
These indicate persistent disease, which is another term for acute HIV infection.
Chronic HIV infection (latent stage)
After the initial acute symptoms pass, the virus enters a chronic or clinical latent stage, where it continues to reproduce but causes no symptoms.
As the infection becomes worse, symptoms also may worsen, including:
- Persistent fever
- Weight loss
- Chronic diarrhea
- Night sweats
- Oral thrush
- Recurrent infections
Differences:
- In HIV-1, these symptoms appear earlier and more severely.
- In HIV-2, the onset is slower, and many individuals remain asymptomatic for years.
Diagnosis: How to Detect the Strains
Diagnosis of both types of HIV strains is essential to start treatment with right treatment approach and to prevent transmission. However, both viruses show similar symptoms but the diagnostic approach is little different. Standard HIV tests are often more sensitive to HIV-1 than HIV-2.
Screening Tests (Initial Detection)
Screening tests are the first step in diagnosis that used to detect the presence of HIV infection in the blood.
The most common tests include:
- Antibody Tests:
These tests detect antibodies that develop by the body in reaction to HIV infection. Usually, samples of either oral or blood fluid are used for them. Sometimes it can take a couple of weeks after exposure for antibodies to appear this is often referred to as the window period. - Antigen/Antibody Combination Tests (4th Generation Tests):
Nowadays, the most common tests are these ones. They can detect HIV antibodies and also the HIV p24 antigen, which is a form of the virus.
While it is slightly more sensitive to HIV-1, this test can detect both HIV-1 and HIV-2 and can detect infection earlier than an antibody-only test.
Confirmatory Tests (To Identify the Type: HIV-1 or HIV-2)
To determine the exact strain, a confirmatory test is carried out if the first screening test reports out positive
- HIV-1/HIV-2 Differentiation Immunoassay:
This test distinguishes between HIV-1 and HIV-2 and confirms the infection. With less time and more accurate outcomes, it replaces the older Western Blot procedure. - Nucleic Acid Test (NAT):
Genetic material (RNA) of the virus can be directly detected by this test. Even in the early stages it can detect the infection, before antibodies develop. In order to manage treatment, NAT also helps in monitoring the viral load, or the concentration of virus in the blood.
CD4 Count and Viral Load Tests (After Diagnosis)
Once an HIV infection is confirmed, doctors measure:
- CD4 Cell Count: It shows the degree of immune system damage.
- Viral Load: Shows the rate at which the virus is multiplying within the body.
Regular monitoring helps in determining the efficacy of the treatment.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to other people and allows immediate treatment, which helps to prevent the progression of AIDS. A lot of hospitals, clinics, and community health centers provide rapid and confidential testing.
Treatment Options for HIV-1 and HIV-2

Both HIV-1 & HIV-2 can be managed with the help of Antiretroviral Therapy (ART). It is a combination of drugs that work by suppressing viral replication, improving immune function, and preventing progression to AIDS. There are various medicine such as Instgra 50mg Tablet, Hepbest 25mg Tablet, Tafero - EM, Viraday Tablet, and Tafero 25mg Tablet that can used in the treatment of both HIV-1 and HIV-2.
HIV-1 Treatment
- Integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs): A key component of modern HIV-1 treatment are integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), which include medicines like bictegravir, dolutegravir, & raltegravir.
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs): The key component of most medical treatments are nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) which include various drugs.
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs): The class of drugs known as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are usually prescribed in combination with other medications.
HIV-2 Treatment
- Integrase inhibitors: It is Commonly used medicines and very effective against HIV-2.
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs): HIV-2 can be successfully treated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
- Protease inhibitors (PIs): Some of these drugs like higher levels of darunavir, prove beneficial against HIV-2 and can be used in various combinations.
Point to remember:
Patients should never self-medicate. Medicines used in the treatment must be prescribed by doctor after confirming the type and stage of infection.
Modern ART Benefits:
- Reduces viral load to undetectable levels
- Prevents transmission (“Undetectable = Untransmittable”)
- Improves quality and length of life
Global Prevalence and Statistics (2025)
According to the UNAIDS 2025 report:
- The UNAIDS 2025 report claims that 39 million people worldwide are HIV positive.
- About 95–98% of infections are caused by HIV-1, which remains to be the most common virus worldwide.
- Most of HIV-2 infections take place in West Africa, especially in Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, & Ivory Coast.
- India has an estimated 2.4 million people living with HIV, with HIV-1 subtype C being the most common form.
- Nearly 77% of people globally are receiving ART, which is a major improvement in HIV care.
Some factors like stigma, missed diagnoses, & treatment resistance remain despite improvements. Controlling the spread of HIV still requires ongoing education and awareness.
Prevention and Awareness
Even while HIV therapy has improved greatly, the best way to prevent new infections is still prevention.
1. Safe Sexual Practices
- Always use condoms properly and routinely when performing protected sexual activity.
- Get regularly tested for HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases, especially when you engage in sexual activity.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners will help you avoid HIV infection.
2. Avoid Sharing Needles
Don't share tattoo needles or injections.
3. Mother-to-Child Prevention
ART can help HIV-positive mothers to prevent transmission during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
4. Pre-Exposure and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis): Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis, or PrEP, is a medication administered to prevent HIV infection in high-risk individuals.
PEP (Post-Exposure Prophylaxis): Within 72 hours after possible exposure emergency treatment should be started.
5. Regular Testing and Counseling
Early diagnosis is important in order to ensures timely treatment and prevents further transmission.
Conclusion
It is important to understand the difference between HIV-1 and HIV-2 for accurate diagnosis, effective & right treatment approach, and awareness. While HIV-1 is the most common and aggressive strain globally and HIV-2 is less common and primarily found in West Africa.
With modern treatment strategies HIV is no longer a death sentence. As this infection is serious and life threatening that needs immediate medical attention otherwise it can be fatal. For buying medicine to treat and manage this infection you should choose safe and trustworthy option like Magicine Pharma. We offer our services on a global level in different regions, including Africa, Latin America, Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and many more.
We can move closer to an HIV free world with the help of awareness, prevention, and early detection.
FAQs
1. Can a person be infected with both HIV-1 and HIV-2 altogether?
A-This condition is rare but yes some individuals can be co-infected with both types. It can take place especially in regions where both strains are prevalent.
2. Is HIV-2 strain infection less aggressive than HIV-1?
A-Yes HIV-2 progresses more slowly & it is less transmissible. But if left untreated it also can lead to AIDS and other serious infections.
3. Can HIV-2 be cured naturally or through herbal medicines?
A-No, it is a serious illness that can't be cured naturally at any cost. It can only control and manage with the help of antiretroviral therapy.
4. Are both HIV-1 and HIV-2 can be detected by the same test?
A-Yes Modern 4th-generation HIV tests can detect both strains. However, additional testing is required to differentiate between them.
5. Is there a vaccine available for HIV infection?
A-Till now there is no approved vaccine available for HIV. Although research is ongoing globally.
References:
World Health Organization (WHO) – HIV/AIDS Fact Sheets (2025)
UNAIDS Global Report 2025
CDC: Differences between HIV-1 and HIV-2
NIH: Antiretroviral Therapy Guidelines 2024